JUN (V-Jun sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog (avian))
2003-01-01 Fei Chen AffiliationHealth Effects Laboratory Division, NIOSH, 1095 Willowdale Rd, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA
Identity
HGNC
LOCATION
1p32.1
LOCUSID
ALIAS
AP-1,AP1,c-Jun,cJUN,p39
FUSION GENES
DNA/RNA
Description
The Jun gene maps on chromosome 1p32-p31 spanning 333799bp. The study by Hattori et al suggested that the Jun gene has no introns.
Transcription
Due to 5 and 3 heterogeneities, several transcripts of Jun mRNA has been identified. The predicted molecular weight of JUN protein is 41.9 kD.
Proteins
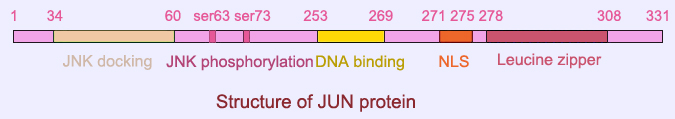
Description
The JUN protein was originally identified as an oncoprotein encoded by a cellular insert in the genome of avian sarcoma virus 17. Following studies demonstrated that JUN is a critical component of AP-1 transcription factor that recognizes the palindromic DNA sequence TGAC/GTCA, the so-called TPA response element (TRE), in the promoter or intron region of a number of genes. JUN can stably associate with itself or Fos protein to form AP-1 complex. JUN can also interact with some activating transcription factor (ATF) members, such as ATF2, ATF3 and ATF4, to form heterodimers that bind to the cAMP-responsive element (CRE) DNA sequence, TGACGTCA.
All JUN proteins from different species contain a N-terminal JNK docking domain (delta domain) adjacent to the JNK phosphorylating site Ser63/73. In the C-terminal, there is a basic domain for DNA binding, followed by a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a leucine zipper motif for dimerization with partner proteins.
Expression
Ubiquitously expressed.
Localisation
Nuclear and mitochondria.
Function
JUN is the most important component of AP-1 transcription factors, and its transcriptional activity is possibly attenuated by JUNB or JUND. It has been well accepted that JUN regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and transformation.
JUN promotes cell cycle transition from G1 phase to S phase by up-regulating cyclin D1 expression and antagonizing the function of p53and p21.
The JUN protein is involved in both the induction and prevention of apoptosis, possibly dependent on the types and development stages of cells. JUN-dependent induction of pro-apoptotic protein FasL and Bim has been demonstrated in several experimental systems. However, evidence indicating an anti-apoptotic activity of JUN has also been provided by the fact that deficiency of Jun gene causes massive hepatocyte apoptosis.
The potential oncogenic transformation of JUN has been revealed by overexpression experiments. This effect of JUN may partially through the induction of certain JUN targeting genes, such as heparin-bind epidermal growth factor-like growth factor (HB-EGF), proliferin and Jun-activated gene in chicken embryo fibroblasts (JAC).
Implicated in
Entity name
Inflammation
Entity name
cancer
Oncogenesis
Overexpression of JUN has been observed in certain human cancer. However, no mutation, rearrangement or amplification of Jun gene has been reported.
Article Bibliography
Other Information
Locus ID:
NCBI: 3725
MIM: 165160
HGNC: 6204
Ensembl: ENSG00000177606
Variants:
dbSNP: 3725
ClinVar: 3725
TCGA: ENSG00000177606
COSMIC: JUN
RNA/Proteins
Expression (GTEx)
Pathways
Protein levels (Protein atlas)
PharmGKB
References
Citation
Fei Chen
JUN (V-Jun sarcoma virus 17 oncogene homolog (avian))
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2003-01-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/gene/151/jun