MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate)
2012-11-01 Atsuhiro Tanabe , Maho Saito AffiliationDivision of Biochemistry, Department of Bioscience, Engineering, Shibaura Institute of Technology, Saitama, Japan
Identity
HGNC
LOCATION
6q21
IMAGE

LEGEND
Figure 1. A) MARCKS location on chromosome 6 is indicated. MARCKS gene starts at 114178527 and ends at 114184652. B) MARCKS gene is indicated. It has two exons and one intron.
LOCUSID
ALIAS
80K-L,MACS,PKCSL,PRKCSL
FUSION GENES
DNA/RNA
Note
The MARCKS gene is located 6q21 (114178527..114184652).
Transcription
The transcription product is 6,1 kb with 2 exons. The mRNA has 996 bp open reading frame. The promoter region has no TATA box and contained multiple transcription initiation sites in a region spanning 57 base pairs (bp) (Harlan et al., 1991).
Proteins
Note
MARCKS was cloned as a protein kinase C (PKC) substrate. The protein binds plasma membrane via N-terminus myristoylation and the phosphorylation site domain (PSD), which is also called effector domain (ED), with electrostatic interaction. MARCKS interacts with actin, calmodulin, PIP2 on the PSD.
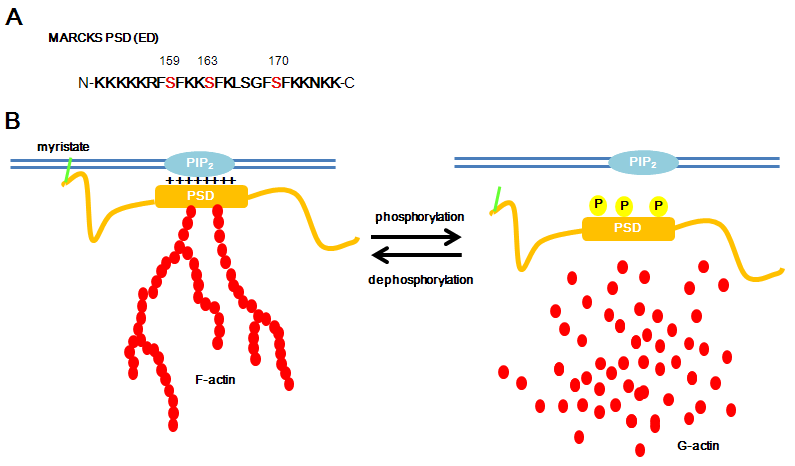
Figure 2. A) MARCKS phosphorylation site domain (PSD (also called effector domain (ED)) is shown. It is mainly consisted of basic amino asids (K and R) and has serin residues phosphorylatable by PKC (159, 163 and 170) and by ROCK (at least 159). B) Dephospho MARCKS binds to plasma membrane and cross-links actin. Phospho MARCKS detached from plasma membrane and disrupts actin filaments.
Description
Phosphorylation of MARCKS is instrumental in its redistribution. MARCKS possesses a basic phosphorylation site domain (PSD). Phosphorylation of this PSD domain prevents the electrostatic interaction of the effector region of the MARCKS to the plasma membrane (George and Blackshear, 1992; Taniguchi and Manenti, 1993; Kim et al., 1994).
Expression
The MARCKS protein is highly expressed in the brain, spleen, and lung, and is virtually absent in skeletal muscle and liver in adult animal (Stumpo et al., 1989; Blackshear et al., 1986; Albert et al., 1986).
Localisation
Dephosphorylated and phosphorylated MARCKS are located at plasma membrane and in cytosol, respectively.
Function
MARCKS closs-links actin filament (Yarmola et al., 2001) and changes cell morphology responsing to cell stimulations in its phosphorylation/dephosphorylation-dependent manner (Tanabe et al., 2012). MARCKS participates in thrombin-induced noradrenaline release from platelets (Elzagallaai et al., 2001) and PMA- or bonbesin-induced neurotensin release from BON cells (Li et al., 2005). MARCKS regulates the proliferation and/or movement of some type of cells (Brooks et al.,1996; Zhao et al., 2000; Weimer et al., 2009). MARCKS plays a vital role in the normal developmental processes of neurulation, hemisphere fusion, forebrain commissure formation, and formation of cortical and retinal laminations (Stumpo et al., 1995). Long-term potentiation (LTP) is significantly impaired in the mossy fiber-CA3 pathway in MARCKS heterozygous mutant mice (Hussain et al., 2006).
Homology
Human MARCKS protein (332 amino acids) was approximately 89, 74, and 59% identical to the bovine, mouse, and chicken proteins. N-terminal domain and phosphorylation site domain (PSD) are highly-conserved between species (from human to Xenopus).
Implicated in
Entity name
Melanoma
Note
In MARCKS over expressed human tumor-derived choroidal melanoma cells (OCM-1) the growth was reduced by 35-40% when compared with control cells (Manenti et al., 1998). In a highly motile melanoma cell line WM-1617 melanoma cells nonphosphorylated MARCKS works as an adhesion stabilizer (Estrada-Bernal et al., 2009).
Entity name
Alzheimer disease (AD)
Note
PKC-induced phosphorylation of MARCKS in cortical neurons in AD brains was weaker than that in control brains. However, phosphorylation of MARCKS was detected in microglia and dystrophic neurites within neuritic plaques (Kimura et al., 2000). In microglia amyloid β induces phosphorylation of MARCKS through mitogen-activatd protein kinase (MAPK) (Hasegawa et al., 2001) and PKCδ (Nakai et al., 2001).
Article Bibliography
Other Information
Locus ID:
NCBI: 4082
MIM: 177061
HGNC: 6759
Ensembl: ENSG00000277443
Variants:
dbSNP: 4082
ClinVar: 4082
TCGA: ENSG00000277443
COSMIC: MARCKS
RNA/Proteins
Expression (GTEx)
Pathways
Protein levels (Protein atlas)
References
Citation
Atsuhiro Tanabe ; Maho Saito
MARCKS (myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate)
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2012-11-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/gene/50926/marcks