NFKB1 (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1)
2002-01-01 Fei Chen AffiliationHealth Effects Laboratory Division, NIOSH, 1095 Willowdale Rd, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA
Identity
HGNC
LOCATION
4q24
LOCUSID
ALIAS
CVID12,EBP-1,KBF1,NF-kB,NF-kB1,NF-kappa-B1,NF-kappaB,NF-kappabeta,NFKB-p105,NFKB-p50,NFkappaB
FUSION GENES
DNA/RNA
Description
The gene encoding human nfkb1 has 24 exons spanning 156 kb. The expression of nfkb1 can be positively regulated by NF-kB itself and possibly Ets family transcription factors.
Proteins
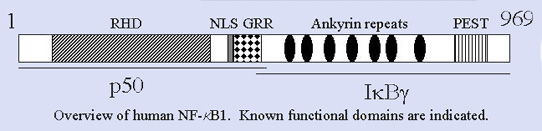
Description
The nfkb1 gene encodes a protein composed 968 amino acids with an approximately molecular weight of 105 kDa, which was considered as a precursor of p50 subunit of NF-kB complexes. In the N-terminal region of NF-kB1, there is a Rel homology domain (RHD) composed of ~300 amino acids that are responsible for DNA binding, dimerization with other Rel family members, and interaction with IkB proteins. The C-terminal region of NF-kB1 contains multiple copies of the so-called ankyrin repeats which is found in IkB family members, including IkBa, IkBb, IkBe, Bcl3, and Drosophila cactus. The earlier studies by several groups demonstrated that NF-kB1 was posttranslationally cleaved to produce the p50 molecule through the ubiquitin-proteasome dependent degradation of the C-terminal portion of NF-kB1. Further studies by Lin and Ghosh suggested that a glycine-rich region (GRR) within the region of 375 to 400 of NF-kB1 is necessary and sufficient for directing the cleavage of NF-kB1. However, recent studies challenged this model and revealed a novel mechanism in which p50 is generated by a unique cotranslational processing event involving the 26S proteasome. In other words, NF-kB1 is not the precursor of p50.
Expression
nfkb1 is widely expressed in virtually all type of cells in both adults and in the embryo.
Localisation
cytosol, nuclei after activation.
Function
regulation of the genes involved in cell-to-cell interaction, intercellular communication, cell recruitment or transmigration, amplification or spreading of primary pathogenic signals, and initiation or acceleration of tumorigenesis. The full length of NF-kB1 can serve as an endogenous inhibitor for the NF-kB p50/p65(RelA) heterodimer. It has been proposed that the homodimer of NF-kB p50 was transcriptionally inactive in the absence of Bcl3. Furthermore, the NF-kB p50 homodimer may function to competitively inhibit B binding by transactivating NF- B dimers. The Bcl3 protein can form a complex with this homodimer at B sites and act as a transactivator of NF-kB p50 homodimer. Interaction with : members of IkB family and Rel family, LYL1 , Bcl3, NCOA1a(V).
Implicated in
Entity name
cancer (see below), autoimmune arthritis, glomerulonephritis, asthma, inflammatory bowel disease, septic shock, lung fibrosis, HTLV-1 infection, and AIDS.
Oncogenesis
overexpression of nfkb1 has been found in a number of human cancer including non-small cell lung carcinoma, colon cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer, bone cancer and brain cancer. The rearrangement of nfkb1 gene, however, only has been identified in certain acute lymphoblastic leukemias.
Article Bibliography
Other Information
Locus ID:
NCBI: 4790
MIM: 164011
HGNC: 7794
Ensembl: ENSG00000109320
Variants:
dbSNP: 4790
ClinVar: 4790
TCGA: ENSG00000109320
COSMIC: NFKB1
RNA/Proteins
Expression (GTEx)
Pathways
Protein levels (Protein atlas)
PharmGKB
References
Citation
Fei Chen
NFKB1 (nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1)
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2002-01-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/gene/323