MMP9 (matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase))
2006-02-01 Deepak Pralhad Patil , Gopal Chandra Kundu AffiliationNational Center for Cell Science, NCCS Complex, Ganeshkhind, Pune 411007, India
Identity
HGNC
LOCATION
20q13.12
LOCUSID
ALIAS
CLG4B,GELB,MANDP2,MMP-9
FUSION GENES
DNA/RNA
Description
This gene can be found on Chromosome 26 at location: 44,070,954 - 44,078,606.
Transcription
The DNA sequence contains 13 exons and the transcript length: 2,335 bps translated to a 707 residues protein.
Proteins
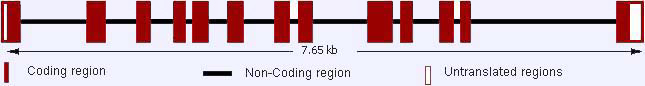
Domain structure of the MMP9.
The hemopexin/vitronectin-like domain contains four repeats with the first and last linked by a disulfide bond.
Description
MMP-9 is a Zn+2 dependent endopeptidase, synthesized and secreted in monomeric form as zymogen. The structure is almost similar to MMP2, another member of matrixmetalloproteinase family. The nascent form of the protein shows an N-terminal signal sequence ("pre" domain) that directs the protein to the endoplasmic reticulum. The pre domain is followed by a propeptide-"pro" domain that maintains enzyme-latency until cleaved or disrupted, and a catalytic domain that contains the conserved zinc-binding region. A hemopexin/vitronectin-like domain is also seen, that is connected to the catalytic domain by a hinge or linker region. The hemopexin domain is involved in TIMP (Tissue Inhibitors of Metallo-Proteinases) binding e.g. TIMP-1 & TIMP-3, the binding of certain substrates, membrane activation, and some proteolytic activities. It also shows a series of three head-to-tail cysteine-rich repeats within its catalytic domain. These inserts resemble the collagen-binding type II repeats of fibronectin and are required to bind and cleave collagen and elastin.
Like other proteolytic enzymes, MMP-9 is first synthesized as inactive proenzyme or zymogens. Activation of proMMP-9 is mediated by plasminogen activator/plasmin (PA/plasmin) system. The regulation of MMP-9 activity is also controlled through TIMP-3.
Like other proteolytic enzymes, MMP-9 is first synthesized as inactive proenzyme or zymogens. Activation of proMMP-9 is mediated by plasminogen activator/plasmin (PA/plasmin) system. The regulation of MMP-9 activity is also controlled through TIMP-3.
Expression
MMP-9 expression is regulated by several cytokines and growth factors, including interleukins, interferons, EGF (Epidermal growth factor), NGF (Nerve growth factor), basic FGF (Fibroblast growth factor), VEGF (Vascular endothelial growth factor), PDGF (Platelet derived growth), TNF-a (Tumor necrosis factor), TGF-b (Tranforming growth factor), the extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN and also osteopontin. Many of these stimuli induce the expression and/or activation of c-fos and c-jun proto-oncogene products, which heterodimerize and bind activator protein-1 (AP-1) sites within of MMP9 gene promoters.
Localisation
Peri/extracellular
Function
Primary function is degradation of proteins in the extracellular matrix. It proteolytically digests decorin, elastin, fibrillin, laminin, gelatin (denatured collagen), and types IV, V, XI and XVI collagen and also activates growth factors like proTGFb and proTNFa. Physiologically, MMP-9 in coordination with other MMPs, play a role in normal tissue remodeling events such as neurite gowth, embryonic development, angiogenesis, ovulation, mammary gland involution and wound healing. MMP-9 with other MMPs is also involved in osteoblastic bone formation and/or inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption.
Homology
Homology in amino acid sequence is seen with the other members of Metalloproteinase family especially with MMP-2.
Mutations
Germinal
Not yet reported.
Implicated in
Entity name
Invasive and highly tumorigenic cancers
Disease
Elevated expression of MMP-9, along with MMP-2 is usually seen in invasive and highly tumorigenic cancers such as colorectal tumors, gastric carcinoma, pancreatic carcinoma, breast cancer, oral cancer, melanoma, malignant gliomas, chondrosarcoma, gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. Levels are also increased in malignant astrocytomas, carcinomatous meningitis, and brain metastases.
Oncogenesis
MMPs promote tumor progression and metastasis in invasive cancers by degradation of the ECM (ExtraCellular Matrix), which consists of two main components: Basement membranes and interstitial connective tissue. Though ECM comprises of many proteins (laminin-5, proteoglycans, entactin, osteonectin) collagen IV is the major element. MMP-2 & MMP-9 efficiently degrade collagen IV and laminin-5 thereby, assisting the metastatic cancerous cells to pass through the basement membrane. The degradation of ECM not only assists migration of metastatic cancerous cells, but also allows enhanced tumor growth by providing necessary space. Further, it is noteworthy that the ratio of active to latent form of MMP-9 increased with tumor progression in invasive cancers. MMP-9, with its family members also promotes angiogenesis (a critical process required for tumor cell survival) by degrading the vascular basement membrane interstitium and also by releasing sequestered VEGF, which is a well know angiogenic molecule. Localization of MMP9 to the cell surface is required to promote tumor invasion and angiogenesis.
Entity name
Arthritis, autosomal recessive osteolysis disorder, coronary artery disease, pulmonary-emphysema and diabetic retinopathy.
Article Bibliography
Other Information
Locus ID:
NCBI: 4318
MIM: 120361
HGNC: 7176
Ensembl: ENSG00000100985
Variants:
dbSNP: 4318
ClinVar: 4318
TCGA: ENSG00000100985
COSMIC: MMP9
RNA/Proteins
Expression (GTEx)
Pathways
Protein levels (Protein atlas)
PharmGKB
References
Citation
Deepak Pralhad Patil ; Gopal Chandra Kundu
MMP9 (matrix metallopeptidase 9 (gelatinase B, 92kDa gelatinase, 92kDa type IV collagenase))
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2006-02-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/gene/41408/mmp9-(matrix-metallopeptidase-9-(gelatinase-b-92kda-gelatinase-92kda-type-iv-collagenase))