Clinics and Pathology
Disease
myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML); they may occur de novo, or be secondary to an exposure to chemical mutagens or to chemotherapy treatments with alkylating agents; may probably also be secondary to immunosuppressive therapy for severe aplastic anemia
Phenotype stem cell origin
Epidemiology
-7 is the most frequent abnormality in secondary myeloid disorders, found in 51% of the cases in a series of 246 cases, while del(7q) was found in 7%, and a partial monosomy 7 as a result of an unbalanced translocation in 8% of cases; in contrast, -7/del(7q) is found in 10% of de novo myeloid disorders; the sex ratio is 1.5 male for 1 female; the proportion of adults with a -7 myeloid disorder grows dramatically after 60 years
Clinics
characterized by infectious susceptibility, quick aggravation, and treatment resistance
Prognosis
monosomy 7 is classified as a poor prognostic criterium by the International Prognostic Scoring System; the actuarial relapse rate at one year is 82 %, and the 7-yr actuarial event-free survival is 6 %; after an allogeneic bone marrow transplantation, -7 is predictive of an unfavorable outcome
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics morphological
deletion (7q) is always interstitial; cluster of breakpoints in 7q11 to 7q36, is a with two common minimal zones in q22 and in q32-34
Cytogenetics molecular
using loss of heterogygocity (LOH) studies and YAC libraries, a 2 to 3 Mb segment in 7q22 has been designated as the proximal common deleted area; the 7q33-34 zone is the consensual area for the distal deletion; LOH studies suggest that a specific mechanism, such as mitotic recombination in bone marrow stem cell leading to homozygosity in both granulocytes and lymphocytes, may be implicated
Additional anomalies
-5/del(5q), found in 40 to 60 % of the secondary MDS cases; trisomy 8
Variants
the balanced translocation t(1;7)(q10;p10), and many unbalanced translocation, having for consequence a partial monosomy 7 of the 7q22 to 7q34 bands may, in a way, be considered as variants
Genes Involved and Proteins
Note
-7/del(7q) is not only frequent in secondary MDS or AML, but also in leukemias occurring in individuals with constitutional syndromes including predisposition to myeloid disorders; these findings suggest the presence of a putative myeloid leukemia suppressor gene in the commonly deleted genomic segment 7q22 and even multiple genes in 7q22 -31.1 that are playing a role in leukemogenesis; ASNS (asparagine synthetase gene) in 7q21.3-q22.1; ACHE (acetyl cholinesterase), EPO (erythropoietin), PLANH1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor 1) in 7q22; and MET in 7q31.2-31.3
candidate genes are :
Article Bibliography
Summary
Note
-7/del(7q) in childhood blood malignancies exhibits a specific pattern of pathogenesis; chromosome 7 anomalies are not rare in acute lymphocytic leukaemia (ALL); they occur in balanced translocations involving 7p15 or 7q34 in T lineage and 7q22 or 7q32 in B proliferations; monosomy 7 is present in 5 to 6 % of ALL, most often as a secondary anomaly of the t(9;22); the association t(9;22), -7 is present in 16 % of the Ph1+ ALL, i.e. in 3% of ALL as a whole; we will hereunder focuse on -7/del(7q) in adult myeloproliferations
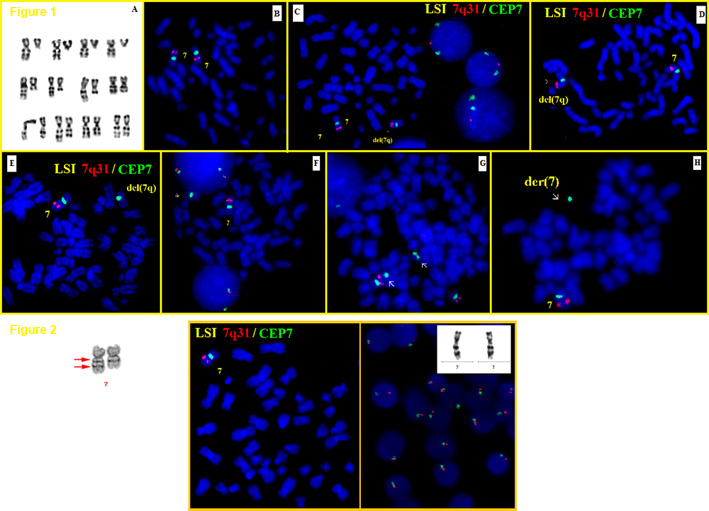
del(7q) Figure 1: Partial karyotypes with 7q deletions (A). Fluorescence in situ hybridization with Vysis D7S486 (7q31)/CEP 7 probe (Abbott moleculars, US) showing 2 green and 2 red signals on normal and one red signal in abnormal metaphases indicating 7q deletion of various sizes (C-H) u2013 Courtesy Adriana Zamecnikova. Figure 2: del(7q) G- banding - Courtesy Jean-Luc Lai and Alain Vanderhaegen; Hybridization with Vysis D7S486 (7q31)/CEP 7 probe (Abbott moleculars, US) showing 1 green and 1 red signal confirming monosomy 7on metaphase and interphase cells u2013 Courtesy Adriana Zamecnikova.
Citation
François Desangles
-7/del(7q) in adults
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 1999-06-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/haematological/1093/7-del(7q)-in-adults