TIMP2 (TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2)
2008-04-01 Demitrios H Vynios AffiliationLaboratory of Biochemistry, Department of Chemistry, School of Natural Sciences, University of Patras, 265 00 Patras, Greece
DNA/RNA
Note
Comparison of the cDNA sequences of human TIMP2 with human TIMP1 shows little homology considering that seen at the amino acid level. This result implies that these genes diverged early in the evolution of this gene family.

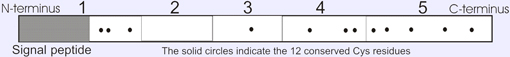
The translated parts of exons 1-5 are shown by black boxes. The introns are shown by lines. The 5 UTR and the 3 UTR regions are shown by white boxes.
Description
The TIMP2 gene contains five exons and spans 72,413 bases (start 74,360,654 bp to end 74,433,067 from 17pter) oriented at the minus strand. The exons are separated by four introns of 54.8, 2.7, 9.1, and 1.7 kb.
Transcription
Two transcripts of 1.2 and 3.8 kb are reported. Their difference in size is the result of the use of different polyadenylation signals within the 3-end of the gene. There is no evidence of alternatively spliced products.
Proteins
Note
The proteins encoded by this gene family are natural inhibitors of the matrix metalloproteinases, a group of peptidases involved in degradation of the extracellular matrix. In addition to this role, the encoded protein has a unique role among TIMP family members in its ability to directly suppress the proliferation of endothelial cells. As a result, the encoded protein may be critical to the maintenance of tissue homeostasis by suppressing the proliferation of quiescent tissues in response to angiogenic factors, and by inhibiting protease activity in tissues undergoing remodelling of the extracellular matrix.
Description
Propeptide: Size 220 amino acids; Molecular mass 24.4 kDa.
Mature protein: Size 194 amino acids; Molecular mass 21 kDa.
It belongs to the protease inhibitor I35 (TIMP) family.
It contains 1 NTR domain. No N- glycosylation is observed.
Mature protein: Size 194 amino acids; Molecular mass 21 kDa.
It belongs to the protease inhibitor I35 (TIMP) family.
It contains 1 NTR domain. No N- glycosylation is observed.
Expression
Constitutive.
Localisation
Secreted protein, as well as cell surface bound.
Function
A variety of distinct functions have been described so far:
1. TIMP2 complexes with some of enzymes of metalloproteinases family and irreversibly inactivates them. It is known to act on MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-7, MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-10, MMP-13, MMP-14, MMP-15, MMP-16 and MMP-19, through its tight binding to the enzymes in a 1:1 stoichiometry with a Ki ‹ 10-9 M. The complex between human proMMP-2 and TIMP-2 is well studied and its crystal structure reveals an interaction between the hemopexin domain of proMMP-2 and the C-terminal domain of TIMP2, leaving the catalytic site of MMP-2 and the inhibitory site of TIMP2 distant and spatially isolated. The activity of TIMP2 is dependent on the presence of disulfide bonds in its structure.
2. TIMP2 is a positive regulator of MMP-14 (MT1-MMP) by promoting the availability of the enzyme at the cell surface and supporting pericellular proteolysis (after forming the trimolecular complex of MMP-14, TIMP-2 and proMMP-2). Through this activity of TIMP2 the specific activation of proMMP-2, after the interaction of TIMP2 with MT1-MMP (possibly MT2-MMP and MT3-MMP) in cell surface, is achieved.
3. Inhibition of angiogenesis, after binding to alpha3 / beta1-integrin, resulting in a decreased association of the protein tyrosine phosphatase Shp-1 with beta1-integrin subunits and increased association of Shp-1 with tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors (both VEGFR-2 and EGFR-1).
4. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation. This activity is localized to TIMP2 C-terminal domain, specifically to the C-terminal disulfide loop, referred to as loop 6.
5. Antiapoptotic activity.
6. TIMP2 has been found to block tumor cell invasion both in vitro and in vivo and may act as metastasis suppressor gene.
Homology
TIMP2 shares 40% aminoacid sequence homology with TIMP1 especially in the N-terminal domain.
Implicated in
Entity name
Cancer
Note
TIMP2 possesses a complicated role in cancer through its ability to regulate MT1-MMP activity and to inhibit MMPs, especially MMP-2. Its function as inhibitor of angiogenesis; which is independent to the previous, suggests a negative role in cancer. In addition, allelic deletion at 17q23-25 is found in approximately one-third of breast cancer patients and it has been proposed that TIMP2 may act as metastasis suppressor gene.
Article Bibliography
Other Information
Locus ID:
NCBI: 7077
MIM: 188825
HGNC: 11821
Ensembl: ENSG00000035862
Variants:
dbSNP: 7077
ClinVar: 7077
TCGA: ENSG00000035862
COSMIC: TIMP2
RNA/Proteins
Expression (GTEx)
Pathways
Protein levels (Protein atlas)
References
Citation
Demitrios H Vynios
TIMP2 (TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2)
Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2008-04-01
Online version: http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org/gene/42572/js/js/lib/deep-insight-explorer